Folkman's theorem, Ken Brown's lemma, and Solving Recurrences in Double Free set Chern Class Degrees of Freedom with Schubert calculus
Folkman's theorem is a theorem in mathematics, and more particularly in arithmetic combinatorics and Ramsey theory. According to this theorem, whenever the natural numbers are partitioned
into finitely many subsets, there exist arbitrarily large sets of
numbers all of whose sums belong to the same subset of the partition. The theorem had been discovered and proved independently by several mathematicians, before it was named "Folkman's theorem", as a memorial to Jon Folkman, by Graham, Rothschild, and Spencer.
The integer version can be deduced from the set version by considering colourings which depend only on the number of 1s of the string. The integer version can also be deduced from Rado's theorem.
The set version can be deduced from the integer version by using Ramsey's Theorem to restrict to a coloring which depends only on the cardinality of a set. The set version of this theorem can be deduced from Hindman's theorem. The higher k generalization of this version is the Graham-Rothschild theorem.
Kenneth Stephen Brown (born 1945) is a professor of mathematics at Cornell University, working in category theory and cohomology theory. Among other things, he is known for Ken Brown's lemma in the theory of model categories. He is also the author of the book Cohomology of Groups (Graduate Texts in Mathematics 87, Springer, 1982). The m=2 case of the integer version of this theorem is Schur's theorem
The number of independent ways by which a dynamic system can move, without violating any constraint imposed on it, is called number of degrees of freedom. In other words, the number of degrees of freedom can be defined as the minimum number of independent coordinates that can specify the position of the system completely. Mathematically, degrees of freedom is the number of dimensions of the domain of a random vector, or essentially the number of "free" components (how many components need to be known before the vector is fully determined). In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.
The factorisation lemma is a fundamental tool in the theory of categories of fibrant objects (dually: of cofibrant objects). It mimics one half of the factorisation axioms in a model category in that it asserts that every morphisms may be factored as, in particular, a weak equivalence followed by a fibration.
In mathematics, the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means, or more briefly the AM–GM inequality, states that the arithmetic mean of a list of non-negative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same list; and further, that the two means are equal if and only if every number in the list is the same.
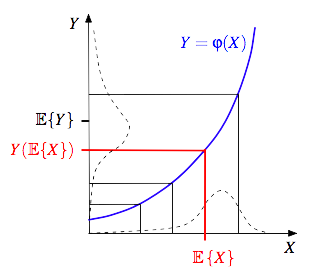
Jensen's inequality can also be proven graphically, as illustrated on the third diagram. The dashed curve along the X axis is the hypothetical distribution of X, while the dashed curve along the Y axis is the corresponding distribution of Y values. Note that the convex mapping Y(X) increasingly "stretches" the distribution for increasing values of X.
As well as a Triple-Free Set, In statistics and uncertainty analysis, the Welch–Satterthwaite equation is used to calculate an approximation to the effective degrees of freedom of a linear combination of independent sample variances, also known as the pooled degrees of freedom, corresponding to the pooled variance.
In the context of complex dynamics, a topic of mathematics, the Julia set and the Fatou set are two complementary sets (Julia "laces" and Fatou "dusts").
In mathematics, in particular in algebraic topology, differential geometry and algebraic geometry, the Chern classes are characteristic classes associated with complex vector bundles.
The HM-GM-AM-QM Inequalities
The geometric mean–arithmetic mean–quadratic mean inequalities.
By Philip Wagala Gwanyama
By David Hirsch
In algebraic geometry, a Schubert variety is a certain subvariety of a Grassmannian, usually with singular points. Like a Grassmannian, it is a kind of moduli space, whose points correspond to certain kinds of subspaces V, specified using linear algebra, inside a fixed vector subspace W. Here W may be a vector space over an arbitrary field, though most commonly over the complex numbers.
To find the harmonic mean of a set of n numbers, add the reciprocals of the numbers in the set, divide the sum by n, then take the reciprocal of the result.
'Lumping turns Calculus on its head. Whereas Calculus analyzes a changing process by dividing it into ever finer intervals, lumping simplifies a changing process by combining it into one unchanging process.' - Street Fighting Mathematics pg. 54 'Lumping, by replacing a curve with a rectangle whose area is easily computed, is already a pictorial analysis.' (Summing series) pg. 73
In mathematics, Schubert calculus is a branch of algebraic geometry introduced in the nineteenth century by Hermann Schubert, in order to solve various counting problems of projective geometry (part of enumerative geometry). It was a precursor of several more modern theories, for example characteristic classes, and in particular its algorithmic aspects are still of current interest. The phrase "Schubert calculus" is sometimes used to mean the enumerative geometry of linear subspaces, roughly equivalent to describing the cohomology ring of Grassmannians, and sometimes used to mean the more general enumerative geometry of nonlinear varieties.
Thanks for your help uncle David Schubert. The Grassmannian is greener on the other side. Green's theorem is a vector identity which is equivalent to the curl theorem in the plane. In mathematics, the Grassmannian Gr is a space which parametrizes all k-dimensional linear subspaces of the n-dimensional vector space V.
The objects introduced by Schubert are the Schubert cells, which are locally closed sets in a Grassmannian defined by conditions of incidence of a linear subspace in projective space with a given flag. For details see Schubert variety.
In mathematics, a characteristic class is a way of associating to each principal bundle X a cohomology class of X. The cohomology class measures the extent the bundle is "twisted" — and whether it possesses sections. Characteristic classes are global invariants that measure the deviation of a local product structure from a global product structure. They are one of the unifying geometric concepts in algebraic topology, differential geometry, and algebraic geometry.
The Erdős–Turán conjecture is an old unsolved problem in additive number theory (not to be confused with Erdős conjecture on arithmetic progressions) posed by Paul Erdős and Pál Turán in 1941.
In additive number theory, the Skolem–Mahler–Lech theorem states that if a sequence of numbers is generated by a linear recurrence relation, then with finitely many exceptions the positions at which the sequence is zero form a regularly repeating pattern.
The Brent-Salamin formula, also called the Gauss-Salamin formula or Salamin formula, or even the Gauss–Legendre algorithm is a formula that uses the arithmetic-geometric mean to compute pi.
By David Hirsch
In Business News
Acts 24
Van der Waerden test of maximum clique problem with Waring's conjecture upon Van der Walls force
By David Hirsch
Scientists Say They've Found Microplastics in People's Poop, But Don't Worry Just Yet
Brought to you by Dow Chemicals, Dupont, British Petroleum... Capitalists...
Charge it on my plastic... Visa, Amex, Master Card, Dinners Club
By David Hirsch
Hell money is a form of joss paper printed to resemble legal tender bank notes.The notes are not an official form of recognized currency or legal tender since their sole intended purpose is to be offered as burnt offerings to the deceased as a superstitious solution to resolve their ancestors' financial problems.
In economics, Gresham's law is a monetary principle stating that "bad money drives out good".
The use of spirit money (also known as hell money or heaven money) in observing different rituals is deeply rooted in Asian culture. Archaeological evidence of “fake/spirit money” can be seen as far back as circa 1000 B.C.
Are not five sparrows sold for two pennies? And not one of them is forgotten before God.—Luke 12:6
Many have claimed that The Dillinger Escape Plan "pioneered" or even "created" the genre with the release of their debut album 'Calculating Infinity' as mathcore due to its frequent use of complex time signatures, atypical rhythms and unpredictable tempo changes.
Math rock
is a style of indie rock that emerged in the late 1980s in the United
States, influenced by post-hardcore, progressive rock bands such as King
Crimson, and 20th century minimal music composers such as Steve Reich.
Math rock is characterized by complex, atypical rhythmic structures
(including irregular stopping and starting), counterpoint, odd time
signatures, angular melodies, and extended, often dissonant, chords. It
bears similarities to post-rock.
By David Hirsch
Spirit money... Pennies from Heaven, heaven money, hell money...
"Paper is poverty...it is the ghost of money, and not money itself." - 1788 letter to Edward Carrington, US President Thomas Jefferson
"In God We Trust" is the official motto of the United States of America and of the U.S. state of Florida. It was adopted as the nation's motto in 1956 as a replacement or alternative to the unofficial motto of E pluribus unum, which was adopted when the Great Seal of the United States was created and adopted in 1782.
A common convention between the two is freeing Christians slaves from Muslims.
By
Paul Kiernan
August 29, 2018
“The subconscious mind will translate into its physical equivalent, by the most direct and practical method available.” - Napoleon Hill, American self-help author. He is known best for his book Think and Grow Rich (
Rusty is the first and only full-length studio album by American math rock band Rodan. It was released in April 1994 on Quarterstick Records. The album takes its name from its engineer, Bob "Rusty" Weston.
The integer version can be deduced from the set version by considering colourings which depend only on the number of 1s of the string. The integer version can also be deduced from Rado's theorem.
The set version can be deduced from the integer version by using Ramsey's Theorem to restrict to a coloring which depends only on the cardinality of a set. The set version of this theorem can be deduced from Hindman's theorem. The higher k generalization of this version is the Graham-Rothschild theorem.
Kenneth Stephen Brown (born 1945) is a professor of mathematics at Cornell University, working in category theory and cohomology theory. Among other things, he is known for Ken Brown's lemma in the theory of model categories. He is also the author of the book Cohomology of Groups (Graduate Texts in Mathematics 87, Springer, 1982). The m=2 case of the integer version of this theorem is Schur's theorem
Emanuele Frittaion
The number of independent ways by which a dynamic system can move, without violating any constraint imposed on it, is called number of degrees of freedom. In other words, the number of degrees of freedom can be defined as the minimum number of independent coordinates that can specify the position of the system completely. Mathematically, degrees of freedom is the number of dimensions of the domain of a random vector, or essentially the number of "free" components (how many components need to be known before the vector is fully determined). In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.
I can't Believe It's not Random!
Rado’s theorem and Deuber’s theorem
Stress and Cognitive Appraisal
by Lazarus and Folkman
The factorisation lemma is a fundamental tool in the theory of categories of fibrant objects (dually: of cofibrant objects). It mimics one half of the factorisation axioms in a model category in that it asserts that every morphisms may be factored as, in particular, a weak equivalence followed by a fibration.
Double-Free Set
Jensen's inequality states that the value of a concave function of an arithmetic mean is greater than or equal to the arithmetic mean of the function's values. In mathematics, Jensen's inequality, named after the Danish mathematician Johan Jensen, relates the value of a convex function of an integral to the integral of the convex function. It was proven by Jensen in 1906.Jensen's inequality can also be proven graphically, as illustrated on the third diagram. The dashed curve along the X axis is the hypothetical distribution of X, while the dashed curve along the Y axis is the corresponding distribution of Y values. Note that the convex mapping Y(X) increasingly "stretches" the distribution for increasing values of X.
As well as a Triple-Free Set, In statistics and uncertainty analysis, the Welch–Satterthwaite equation is used to calculate an approximation to the effective degrees of freedom of a linear combination of independent sample variances, also known as the pooled degrees of freedom, corresponding to the pooled variance.
In the context of complex dynamics, a topic of mathematics, the Julia set and the Fatou set are two complementary sets (Julia "laces" and Fatou "dusts").
Energy service company innovation research
By David HirschIn mathematics, in particular in algebraic topology, differential geometry and algebraic geometry, the Chern classes are characteristic classes associated with complex vector bundles.
The HM-GM-AM-QM Inequalities
The geometric mean–arithmetic mean–quadratic mean inequalities.
By Philip Wagala Gwanyama
Giving Credit to the Texas Able program: Pricing Revolution
By David Hirsch
In algebraic geometry, a Schubert variety is a certain subvariety of a Grassmannian, usually with singular points. Like a Grassmannian, it is a kind of moduli space, whose points correspond to certain kinds of subspaces V, specified using linear algebra, inside a fixed vector subspace W. Here W may be a vector space over an arbitrary field, though most commonly over the complex numbers.
To find the harmonic mean of a set of n numbers, add the reciprocals of the numbers in the set, divide the sum by n, then take the reciprocal of the result.
'Lumping turns Calculus on its head. Whereas Calculus analyzes a changing process by dividing it into ever finer intervals, lumping simplifies a changing process by combining it into one unchanging process.' - Street Fighting Mathematics pg. 54 'Lumping, by replacing a curve with a rectangle whose area is easily computed, is already a pictorial analysis.' (Summing series) pg. 73
In mathematics, Schubert calculus is a branch of algebraic geometry introduced in the nineteenth century by Hermann Schubert, in order to solve various counting problems of projective geometry (part of enumerative geometry). It was a precursor of several more modern theories, for example characteristic classes, and in particular its algorithmic aspects are still of current interest. The phrase "Schubert calculus" is sometimes used to mean the enumerative geometry of linear subspaces, roughly equivalent to describing the cohomology ring of Grassmannians, and sometimes used to mean the more general enumerative geometry of nonlinear varieties.
Thanks for your help uncle David Schubert. The Grassmannian is greener on the other side. Green's theorem is a vector identity which is equivalent to the curl theorem in the plane. In mathematics, the Grassmannian Gr is a space which parametrizes all k-dimensional linear subspaces of the n-dimensional vector space V.
The objects introduced by Schubert are the Schubert cells, which are locally closed sets in a Grassmannian defined by conditions of incidence of a linear subspace in projective space with a given flag. For details see Schubert variety.
How To Learn Trigonometry Intuitively
In mathematics, a characteristic class is a way of associating to each principal bundle X a cohomology class of X. The cohomology class measures the extent the bundle is "twisted" — and whether it possesses sections. Characteristic classes are global invariants that measure the deviation of a local product structure from a global product structure. They are one of the unifying geometric concepts in algebraic topology, differential geometry, and algebraic geometry.
Spherical Waves in Higher Dimensions
interactive trig guide
The Erdos and Turan function
The Erdős–Turán conjecture is an old unsolved problem in additive number theory (not to be confused with Erdős conjecture on arithmetic progressions) posed by Paul Erdős and Pál Turán in 1941.
What is Newton Raphson method used for?
The Newton-Raphson method, or Newton Method,
is a powerful technique for solving equations numerically. Like so much
of the differential calculus, it is based on the simple idea of linear
approximation. The Newton Method, properly used, usually homes in on a root with devastating efficiency.
The
Newton-Raphson method (also known as Newton's method) is a way to
quickly find a good approximation for the root of a real-valued function
f(x)=0 f ( x ) = 0 . It uses the idea that a continuous and
differentiable function can be approximated by a straight line tangent to it.
Intuitive Understanding Of Euler’s Formula
The Basel problem is a problem in mathematical analysis with relevance to number theory, first posed by Pietro Mengoli in 1650 and solved by Leonhard Euler in 1734 and read on 5 December 1735 in The Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences.In additive number theory, the Skolem–Mahler–Lech theorem states that if a sequence of numbers is generated by a linear recurrence relation, then with finitely many exceptions the positions at which the sequence is zero form a regularly repeating pattern.
The Brent-Salamin formula, also called the Gauss-Salamin formula or Salamin formula, or even the Gauss–Legendre algorithm is a formula that uses the arithmetic-geometric mean to compute pi.
Series inspired by Brent / Salamin's formula
In mathematics, Machin-like formulae are a popular technique for computing π to a large number of digits.
Solving Recurrence Relations
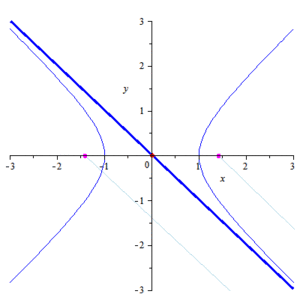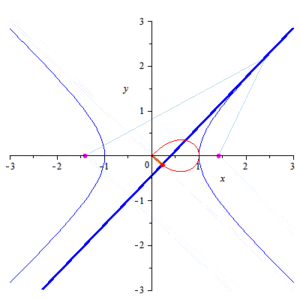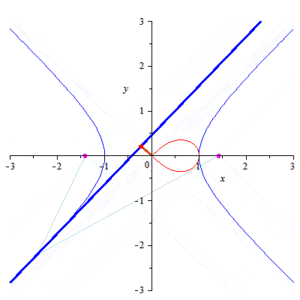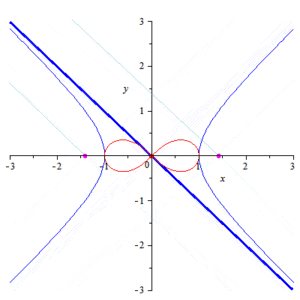
In geometry, the lemniscate of Bernoulli is a plane curve defined from two given points F1 and F2, known as foci, at distance 2a from each other as the locus of points P so that PF1·PF2 = a2. The curve has a shape similar to the numeral 8 and to the ∞ symbol. Its name is from lemniscus, which is Latin for "pendant ribbon". It is a special case of the Cassini oval and is a rational algebraic curve of degree 4.
The lemniscate, also called the lemniscate of Bernoulli, is a polar curve whose most common form is the locus of points the product of whose distances from two fixed points (called the foci) a distance 2a away is the constant a/\2.
In mathematics, the Euler–Maclaurin formula provides a powerful connection between integrals and sums. It can be used to approximate integrals by finite sums, or conversely to evaluate finite sums and infinite series using integrals and the machinery of calculus.
Future-proofing the internet
Quantum computers will break the encryption that protects the internet
For all you h8trs,
A lesson in Heyting algebra for h8trs in the Neighbourhood (mathematics)
By David Hirsch
Doughnut theory? Percolation theory? The smell of Neuropercolation in the morning.
By David Hirsch
OOPs, concepts, OPs, SoD concepts and a separation of concerns
By David Hirsch
Pushing the envelope means testing limits and trying out new, often radical ideas. The expression comes originally from mathematics and engineering, where an envelope is a boundary, but was popularized by test pilots (especially those depicted in Tom Wolfe's novel, The Right Stuff).
No matter how hard you push the envelope, it still stationery. (thanks aunt Anita)
Now apply what you have learned:
Pushing the envelope means testing limits and trying out new, often radical ideas. The expression comes originally from mathematics and engineering, where an envelope is a boundary, but was popularized by test pilots (especially those depicted in Tom Wolfe's novel, The Right Stuff).
A Visual, Intuitive Guide to Imaginary Numbers
Now apply what you have learned:
In Business News
August 22, 2018
U.S. existing home sales fall for fourth straight month
Acts 24
Van der Waerden test of maximum clique problem with Waring's conjecture upon Van der Walls force
By David Hirsch
Scientists Say They've Found Microplastics in People's Poop, But Don't Worry Just Yet
Brought to you by Dow Chemicals, Dupont, British Petroleum... Capitalists...
Charge it on my plastic... Visa, Amex, Master Card, Dinners Club
Fed Plans to Continue Raising Rates, Despite Trump’s Ire
By Binyamin Appelbaum
Kingdom of Kush, Hindu Kush, Asuras (Ahuras) and Devas (Daevas)
Pakistan Says It Dodged U.S. Efforts To Put It On A Terror-Finance List And what the Pakistan Defense web pages state What's Really Behind the Rohingya Crisis in Myanmar as well Oil in Rakhine Basin, gas offshore Myanmar and with aftermath of Clinton's Rice in Sudan, Lebanese president makes landmark visit to Iraq
Zoroastrian Jamsetjee JeeJeebhoy and the opium Astor Sassoons Cohong Kibbutz
By David HirschI am the Walras's law and the Carpenter's Walrasian auction
By David HirschThe Rothschild Ricardo (re) Marx on Corn laws
By David HirschSaudis offer Pakistan $6 billion rescue package to ease economic crisis
By Kay Johnson, Asif ShahzadAdvocacy and policy influencing for social change
Hell money is a form of joss paper printed to resemble legal tender bank notes.The notes are not an official form of recognized currency or legal tender since their sole intended purpose is to be offered as burnt offerings to the deceased as a superstitious solution to resolve their ancestors' financial problems.
Pakistan Islamists protest for second day after Christian acquitted of blasphemy
In economics, Gresham's law is a monetary principle stating that "bad money drives out good".
Nonviolent Action Group (NAG)
Are not two sparrows sold for a penny? And not one of them will fall to the ground apart from your Father.—Matthew 10:29The use of spirit money (also known as hell money or heaven money) in observing different rituals is deeply rooted in Asian culture. Archaeological evidence of “fake/spirit money” can be seen as far back as circa 1000 B.C.
Are not five sparrows sold for two pennies? And not one of them is forgotten before God.—Luke 12:6
Many have claimed that The Dillinger Escape Plan "pioneered" or even "created" the genre with the release of their debut album 'Calculating Infinity' as mathcore due to its frequent use of complex time signatures, atypical rhythms and unpredictable tempo changes.
Indonesia protests after Saudi Arabia executes domestic maid
By Nicola SmithSaudi crown prince jokes about kidnapping Lebanese leader
By Rebecca KheelCapitol Crimes, Abedin, HSBC, Foster, Comey, BCCI, Soros, Myanmar
By David Hirsch
Spirit money... Pennies from Heaven, heaven money, hell money...
The Thirty Sayings of the Wise (Proverbs 22:17-24:22)
Waltke calls Proverbs 22:22-23:11 ”A Decalogue of Sayings About Wealth.”"Paper is poverty...it is the ghost of money, and not money itself." - 1788 letter to Edward Carrington, US President Thomas Jefferson
"In God We Trust" is the official motto of the United States of America and of the U.S. state of Florida. It was adopted as the nation's motto in 1956 as a replacement or alternative to the unofficial motto of E pluribus unum, which was adopted when the Great Seal of the United States was created and adopted in 1782.
Hondurans in migrant caravan sue Trump administration over 'abuse' of power on border policies
By Sarah Harvard
In research recently, I gathered some new understanding of the
Marine Hymn associated as a convention with Our Lady of Good Remedy as
in the year 1198, St. John of Matha
founded the Trinitarians to go to the slave markets, buy the Christian
slaves and set them free:
"From The Halls of Montezuma" refers to the Battle of Chapultepec
on 12/13 September 1847 during the Mexican-American War, where a force
of Marines stormed Chapultepec Castle. The line "To the shores of
Tripoli" refers to the First Barbary War, and specifically the Battle of
Derne in 1805. Barbary slave trade
After Lieutenant Presley O'Bannon and his Marines hoisted the American
flag over the Old World for the first time, the phrase was added to the
flag of the United States Marine Corps.
St. John of Matha, founder of the Trinitarian order and
Home Sales Tumbled In July for the Longest Slump Since 2013
‘Too many would-be buyers are either being priced out or are deciding to postpone their search’
Paul Kiernan
- Business
Global Car Sales Hit Speed Bump as Demand Slows and Trade Tensions Loom
Auto makers grapple with higher steel and aluminum prices and stiffer emissions regulations in Europe and China
“The subconscious mind will translate into its physical equivalent, by the most direct and practical method available.” - Napoleon Hill, American self-help author. He is known best for his book Think and Grow Rich (


Comments
Post a Comment